While my focus has been primarily on academic publication, many of my
papers have been refined and later widely implemented in products and
commercial applications. For example, my work on spherical harmonic
lighting and irradiance environment maps
is now widely included in games (such as the Halo series), and is
increasingly adopted in movie production (being a critical component
of the rendering pipeline in Avatar in 2010, and now an integral part
of RenderMan 16, since mid-2011). These ideas are also being used by
Adobe for relighting, and are now included in many standard textbooks. My research on
importance sampling has inspired a sampling and image-based
lighting pipeline that is becoming standard for production
rendering (also included in RenderMan 16) and is used for example
on the Pixar movie, Monsters University
(my papers discussing production use methods are presented at
EGSR
2012 and the inaugural
JCGT paper).
Models for volumetric scattering have been used in demos by NVIDIA, and elsewhere
in industry. I also participated in developing the first
electronic field guide ; a subsequent iPhone app developed by Prof. Belhumeur and
colleagues is now widely used by the public for visual species identification.
Most recently, work on sampling and reconstruction for rendering (frequency analysis, adaptive wavelet rendering)
has inspired widespread use of Monte Carlo denoising in industry, and
been recognized as seminal in a EG STAR report. Subsequent work on real-time physically-based
rendering and denoising (axis-aligned filtering for soft shadows) has
inspired modern software and hardware real-time AI denoisers, which are now integrated into Optix5 and NVIDIA's RTX chips (2017, 18). As a result, physically-based (raytraced) rendering with denoising is now a reality in both offline and real-time rendering pipelines. Our new Fur Reflectance Model has been used for all animal fur in the 2017 movie War for the Planet of the Apes, nominated for a visual effects Oscar, while new glint models have been used in AutoDesk Fusion 360 and games.
Here is a selection of recent invited talks that give an overview of
research.

|
A Free-Space Diffraction BSDF
SIGGRAPH 2024
We derive an edge-based formulation of Fraunhofer diffraction, which is well suited to the common (triangular) geometric meshes used in computer graphics. Our method dynamically constructs a free-space diffraction BSDF by considering the geometry around the intersection point of a ray of light with an object, and we present an importance sampling strategy for these BSDFs.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Practical Error Estimation for Denoised Monte Carlo Image Synthesis
SIGGRAPH 2024
We present a practical global error estimation technique for Monte Carlo ray tracing combined with deep learning based denoising. Our method uses aggregated estimates of bias and variance to determine the squared error distribution of the pixels, and develops a stopping criterion for an error threshold.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Neural Geometry Fields for Meshes
SIGGRAPH 2024
We present Neural Geometry Fields, a neural representation fordiscrete surface geometry represented by triangle meshes. Our ideais to represent the target surface using a coarse set of quadrangularpatches, and add surface details using coordinate neural networksby displacing the patches.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
A Construct-Optimize Approach to Sparse View Synthesis without Camera Pose
SIGGRAPH 2024
In this paper, we leverage the recent 3D Gaussian splatting method to develop a novel construct-and-optimize method for sparse view synthesis without camera poses. Specifically, we construct a solution progressively by using monocular depth and projecting pixels back into the 3D world. During construction, we optimize the solution by detecting 2D correspondences between training views and the corresponding rendered images. We develop a unified differentiable pipeline for camera registration and adjustment.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Neural Directional Encoding for Efficient and Accurate View-Dependent Appearance Modeling
CVPR 2024
We present Neural Directional Encoding (NDE), a view-dependent appearance encoding of neural radiance fields (NeRF) for rendering specular objects. NDE transfers the concept of feature-grid-based spatial encoding to the angular domain, significantly improving the ability to model high-frequency angular signals.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
What You See is What You GAN: Rendering Every Pixel for High-Fidelity Geometry in 3D GANs
CVPR 2024
In this work, we propose techniques to scale neural volume rendering to the much higher resolution of native 2D images, thereby resolving fine-grained 3D geometry with unprecedented detail. Our approach employs learning-based samplers for accelerating neural rendering for 3D GAN training using up to 5 times fewer depth samples. This enables us to explicitly render every pixel of the full-resolution image during training.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4
|

|
Lift3D: Zero-Shot Lifting of Any 2D Vision Model to 3D
CVPR 2024
In this paper, we ask the question of whether any 2D vision model can be lifted to make 3D consistent predictions. We answer this question in the affirmative; our new Lift3D method trains to predict unseen views on feature spaces generated by a few visual models (i.e. DINO and CLIP), but then generalizes to novel vision operators and tasks, such as style transfer, super-resolution, open vocabulary segmentation and image colorization; for some of these tasks, there is no comparable previous 3D method.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Importance Sampling BRDF Derivatives
TOG 2024
In differentiable rendering, BRDFs are replaced by their differential BRDF counterparts which are real-valued and can have negative values. Our work generalizes BRDF derivative sampling to anisotropic microfacet models, mixture BRDFs, Oren-Nayar, Hanrahan-Krueger, among other analytic BRDFs.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Decorrelating ReSTIR Samplers via MCMC Mutations
TOG 2024
We demonstrate how interleaving Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) mutations with reservoir resampling helps alleviate correlation issues, especially in scenes with glossy materials and difficult-to-sample lighting. Moreover, our approach does not introduce any bias, and in practice we find considerable improvement in image quality with just a single mutation per reservoir sample in each frame.
Paper: PDF Video: M4V Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Conditional Resampled Importance Sampling and ReSTIR
SIGGRAPH Asia 2023
Recent work on generalized resampled importance sampling (GRIS) enables importance-sampled Monte Carlo integration with random variable weights replacing the usual division by probability density. In this paper, we extend GRIS to conditional probability spaces, showing correctness given certain conditional independence between integration variables and their unbiased contribution weights. To show our theory has practical impact, we prototype a modified ReSTIR PT with a final gather pass. This reuses subpaths, postponing reuse at least one bounce along each light path.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4
|

|
Discontinuity-Aware 2D Neural Fields
SIGGRAPH Asia 2023
We construct a feature field that is discontinuous only across known discontinuity locations and smooth everywhere else, and finally decode the features into the signal value using a shallow multi-layer perceptron. We develop a new data structure based on a curved triangular mesh, and demonstrate applications in rendering, simulation and physics-informed neural networks.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4
|

|
OpenIllumination: A Multi-Illumination Dataset for Inverse Rendering Evaluation on Real Objects
NeurIPS 2023
We introduce OpenIllumination, a real-world dataset containing over 108K imagesof 64 objects with diverse materials, captured under 72 camera views and a large number of different illuminations. For each image in the dataset, we provide accurate camera parameters, illumination ground truth, and foreground segmentation masks. Our dataset enables the quantitative evaluation of most inverse rendering and material decomposition methods for real objects.
Paper: PDF
|

|
NeRFs: The Search for the Best 3D Representation
Article for ICBS Frontiers of Science Award 2023
At their core, NeRFs describe a new representation of 3D scenes or 3D geometry. as a continuous volume, with volumetric parameters like view-dependent radiance and volume density obtained by querying a neural network. In this article, we briefly review the NeRF representation, and describe the three decades-long quest to find the best 3D representation for view synthesis and related problems.
Paper: PDF
|

|
A Theory of Topological Derivatives for Inverse Rendering of Geometry
ICCV 2023
We introduce a theoretical framework for differentiable surface evolution that allows discrete topology changes through the use of topological derivatives for variational optimization of image functionals. While prior methods for inverse rendering of geometry rely on silhouette gradients for topology changes, such signals are sparse. In contrast, our theory derives topological derivatives that relate the introduction of vanishing holes and phases to changes in image intensity.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Factorized Inverse Path Tracing for Efficient and Accurate Material-Lighting Estimation
ICCV 2023
We propose a novel Factorized Inverse Path Tracing (FIPT) method which utilizes a factored light transport formulation and finds emitters driven by rendering errors.
Our algorithm enables accurate material and lighting optimization faster than previous work, and is more effective at resolving ambiguities.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Real-Time Radiance Fields for Single-Image Portrait View Synthesis
SIGGRAPH 2023
We present a one-shot method to infer and render a photorealistic 3D representation from a single unposed image (e.g., face portrait) in real-time. Given a single RGB input, our image encoder directly predicts a canonical triplane representation of a neural radiance field for 3D-aware novel view synthesis via volume rendering. Our method is fast (24 fps) on consumer hardware, and produces higher quality results than strong GAN-inversion baselines that require test-time optimization.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
NeuSample: Importance Sampling for Neural Materials
SIGGRAPH 2023
In this paper, we evaluate and compare various pdf-learning approaches for sampling spatially-varying neural materials, and propose new variations for three sampling methods: analytic-lobe mixtures, normalizing flows, and histogram predictions. Our versions of normalizing flows and histogram mixtures perform well and can be used in practical rendering systems for adoption of neural materials in production.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Parameter-Space ReSTIR for Differentiable and Inverse Rendering
SIGGRAPH 2023
We develop an algorithm to reuse Monte Carlo gradient samples between gradient iterations, motivated by reservoir-based temporal importance resampling in forward rendering. We reformulate differential rendering integrals in parameter space, developing a new resampling estimator that treats negative functions, and combines these ideas into a reuse algorithm for inverse texture optimization.
Paper: PDF
|

|
NerfDIFF: Single-image View Synthesis with NeRF-guided Distillation from 3D-aware Diffusion
ICML 2023
Novel view synthesis from a single image requires inferring occluded regions of objects and scenes whilst simultaneously maintaining semantic and physical consistency with the input. In this work, we propose NerfDiff, which addresses this issue by distilling the knowledge of a 3D-aware conditional diffusion model (CDM) into NeRF through synthesizing and refining a set of virtual views at test-time.
Paper: PDF
|

|
View Synthesis of Dynamic Scenes based on Deep 3D Mask Volume
PAMI 2023
We introduce a multi-view video dataset, captured with a custom 10-camera rig in 120FPS. The dataset contains 96 high-quality scenes showing various visual effects and human interactions in outdoor scenes. We develop a new algorithm, Deep 3D Mask Volume, which enables temporally-stable view extrapolation from binocular videos of dynamic scenes, captured by static cameras.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
PVP: Personalized Video Prior for Editable Dynamic Portraits using StyleGAN
EGSR 2023
In this work, our goal is to take as input a monocular video of a face, and create an editable dynamic portrait able to handle extreme head poses. The user can create novel viewpoints, edit the appearance, and animate the face. Our method utilizes pivotal tuning inversion (PTI) to learn a personalized video prior froma monocular video sequence. Then we can input pose and expression coefficients to MLPs and manipulate the latent vectors to synthesize different viewpoints and expressions of the subject.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Neural Free-Viewpoint Relighting for Glossy Indirect Illumination
EGSR 2023
In this paper, we demonstrate a hybrid neural-wavelet PRT solution to high-frequency indirect illumination, including glossy reflection, for relighting with changing view. Specifically, we seek to represent the light transport function in the Haar wavelet basis. For global illumination, we learn the wavelet transport using a small multi-layer perceptron (MLP) applied to a feature field as a function of spatial location and wavelet index, with reflected direction and material parameters being other MLP inputs.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
MesoGAN: Generative Neural Reflectance Shells
CGF 2023 (Presented at EGSR 2023)
We introduce MesoGAN, a model for generative 3D neural textures. This new graphics primitive represents mesoscale appearance by combining the strengths of generative adversarial networks (StyleGAN) and volumetric neural field rendering.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Vision Transformer for NeRF-Based View Synthesis from a Single Input Image
WACV 2023
We leverage both global and local features to form an expressive 3D representation for NeRF-Based view synthesis from a single image. The global features are learned from a vision transformer, while the local features are extracted from a 2D convolutional network.
Paper: PDF
|

|
A Level Set Theory for Neural Implicit Evolution under Explicit Flows
(Best Paper Honorable Mention) ECCV 2022
We present a framework that allows applying deformation operations defined for triangle meshes onto neural implicit surfaces. Our method uses the flow field to deform parametric implicit surfaces by extending the classical theory of level sets.
Paper: PDF
Project: Code/Video
|

|
Physically-Based Editing of Indoor Scene Lighting from a Single Image
ECCV 2022
We present a method to edit complex indoor lighting from a single image. We tackle this problem using novel components: a holistic scene reconstruction method that estimates reflectance and parametric 3D lighting, and a neural rendering framework that re-renders the scene from our predictions. We enable light source insertion, removal and replacement.
Paper: PDF
Project: Code/Video
|

|
Covector Fluids
SIGGRAPH 2022
We propose a new velocity-based fluid solver derived from a reformulated Euler equation using covectors. Our method generates rich vortex dynamics by an advection process that respects the Kelvin circulation theorem. The numerical algorithm requires only a small local adjustment to existing advection-projection methods and can easily leverage recent advances therein. The resulting solver emulates a vortex method without the expensive conversion between vortical variables and velocities.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4 YouTube Code: ZIP
|

|
Rendering Neural Materials on Curved Surfaces
SIGGRAPH 2022
The goal of this paper is to design a neural material representation capable of correctly handling silhouette effects. We extend the neural network query to take surface curvature information as input, while the query output is extended to return a transparency value in addition to reflectance. We train the new neural representation on synthetic data that contains queries spanning a variety of surface curvatures. We show an ability to accurately represent complex silhouette behavior that would traditionally require more expensive and less flexible techniques, such as on-the-fly geometry displacement or ray marching.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Spatiotemporal Blue Noise Masks
EGSR 2022
We propose novel blue noise masks that retain high quality blue noise spatially, yet when animated produce values at each pixel that are well distributed over time. By extending spatial blue noise to spatiotemporal blue noise, we overcome the convergence limitations of prior blue noise works, enabling new applications for blue noise distributions.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
Code and Data: Github Link
|

|
NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
CACM 2022
We present a method that achieves state-of-the-art results for synthesizing
novel views of complex scenes by optimizing an underlying continuous
volumetric scene function using a sparse set of input views. Our algorithm
represents a scene using a fully connected (nonconvolutional) deep network,
whose input is a single continuous 5D coordinate.
Paper: PDF
ECCV 20: PDF Video: MP4 YouTube
|

|
Learning Neural Transmittance for Efficient Rendering of Reflectance Fields
BMVC 2021
We propose a novel method based on precomputed Neural Transmittance Functions to accelerate the rendering of neural reflectance fields. Our neural transmittance functions enable us to efficiently query the transmittance at an arbitrary point in space along an arbitrary ray without tedious ray marching, which effectively reduces the time-complexity of the rendering by up to two orders of magnitude.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Differential Time-Gated Rendering
SIGGRAPH Asia 2021
In this paper, we introduce a new theory of differentiable time-gated
rendering that enjoys the generality of differentiating with respect to
arbitrary scene parameters. Our theory also allows the design of
advanced Monte Carlo estimators capable of handling cameras
with near-delta or discontinuous time gates.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: ZIP
|

|
Deep 3D Mask Volume for View Synthesis of Dynamic Scenes
ICCV 2021
The next key step in immersive virtual experiences is view synthesis of
dynamic scenes. However, several challenges exist due to the lack of
high quality training datasets, and the additional time dimension for
videos of dynamic scenes. To address this issue, we introduce a
multi-view video dataset, captured with a custom 10-camera rig in
120FPS. The dataset contains 96 high-quality scenes showing various
visual effects and human interactions in outdoor scenes. We develop a
new algorithm, Deep 3D Mask Volume, which enables temporally stable view
extrapolation from binocular videos of dynamic scenes, captured by
static cameras.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Modulated Periodic Activations for Generalizable Local Functional Representations
ICCV 2021
We present a new representation that generalizes to multiple instances
and achieves state-of-the-art fidelity. We use a dual-MLP
architecture to encode the signals. A synthesis network creates a
functional mapping from a low-dimensional input (e.g., pixel-position)
to the output domain (e.g. RGB color). A modulation network maps a
latent code corresponding to the target signal to parameters that
modulate the periodic activations of the synthesis network. We also
propose a local functional representation which enables generalization.
Paper: PDF
|

|
NeuMIP: Multi-Resolution Neural Materials
SIGGRAPH 2021
We propose NeuMIP, a neural method for representing and rendering a variety of material appearances at different scales. Classical prefiltering (mipmapping) methods work well on simple material properties such as diffuse color, but fail to generalize to normals, self-shadowing, fibers or more complex structures and reflectances. We develop mipmap pyramids of neural textures to address this problem, along with neural offsets.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Deep Relightable Appearance Models for Animatable Faces
SIGGRAPH 2021
We present a method for building high-fidelity animatable 3D face models that can be posed and rendered with novel lighting environments in real-time. We first train an expensive but generalizable model on point-light illuminations, and use it to generate a training set of high-quality synthetic face images under natural illumination conditions. We then train an efficient model on this augmented dataset.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Kelvin Transformations for Simulations on Infinite Domains
SIGGRAPH 2021
We introduce a general technique to transform a PDE problem on an unbounded
domain to a PDE problem on a bounded domain. Our method uses the Kelvin
Transform, which essentially inverts the distance from the origin.
We factor the desired solution into the product of an analytically known
asymptotic component and another function to solve for, demonstrating
Poisson, Laplace and Helmholtz problems.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Hierarchical Neural Reconstruction for Path Guiding Using Hybrid Path and Photon Samples
SIGGRAPH 2021
We present a hierarchical neural path guiding framework which uses both path and photon samples to reconstruct high-quality sampling distributions. Uniquely, we design a neural network to directly operate on a sparse quadtree, which regresses a high-quality hierarchical sampling distribution. Our novel hierarchical framework enables more fine-grained directional sampling with less memory usage, effectively advancing the practicality and efficiency. This is the
follow-up for the Photon-Driven Neural Reconstruction paper below.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Photon-Driven Neural Reconstruction for Path Guiding
TOG 2021
We present a novel neural path guiding approach that can reconstruct
high-quality sampling distributions for path guiding from a sparse set
of samples, using an offline trained neural network. We
leverage photons traced from light sources as the primary input for
sampling density reconstruction, which is effective for challenging
scenes with strong global illumination. This is the precursor for the
Hierarchical Neural Reconstruction paper above.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Vectorization for Fast, Analytic and Differentiable Visibility
TOG 2021
We develop a new rendering method, vectorization, that computes analytic solutions to 2D point-to-region integrals in conventional ray tracing and rasterization pipelines. Our approach revisits beam tracing and maintains all the visible regions formed by intersections and occlusions in the beam (shown leftmost for primary visibility and shadows).
Paper: PDF
MP4
|

|
Neural Light Transport for Relighting and View Synthesis
TOG 2021
We propose a semi-parametric approach for learning a neural representation of
the light transport of a scene. The light transport is embedded in a texture
atlas of known but possibly rough geometry. We model all non-diffuse and
global light transport as residuals added to a physically-based diffuse
base rendering.
Paper: PDF
MP4
|

|
NeLF: Neural Light-Transport Field for Portrait View Synthesis and Relighting
EGSR 2021
We present a system for portrait view synthesis and relighting: given multiple portraits, we use a neural network to predict the light-transport field in 3D space, and from the predicted Neural Light-transport Field (NeLF) produce a portrait from a new camera view under a new environmental lighting.
Paper: PDF
MOV
|

|
Human Hair Inverse Rendering using Multi-View Photometric Data
EGSR 2021
We introduce a hair inverse rendering framework to reconstruct high-fidelity 3D geometry of human hair, as well as its reflectance,which can be readily used for photorealistic rendering of hair. We demonstrate the accuracy and efficiency of our method using photorealistic synthetichair rendering data.
Paper: PDF
MOV
|

|
Uncalibrated, Two Source Photo-Polarimetric Stereo
PAMI 2021
In this paper we present methods for estimating shape from polarisation and
shading information, i.e. photo-polarimetric shape estimation, under varying,
but unknown, illumination, i.e. in an uncalibrated scenario. We propose
several alternative photo-polarimetric constraints that depend upon the partial
derivatives of the surface and show how to express them in a unified system of
partial differential equations of which previous work is a special case.
Paper: PDF
|

|
OpenRooms: An Open Framework for Photorealistic Indoor Scene Datasets
CVPR 2021
We propose a novel framework for creating large-scale photorealistic
datasets of indoor scenes, with ground truth geometry, material, lighting
and semantics. Our goal is to make the dataset creation process widely
accessible, transforming scans into photorealistic datasets with high-quality
ground truth.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary
MP4
|

|
Real-Time Selfie Video Stabilization
CVPR 2021
We propose a novel real-time selfie video stabilization method that is completely automatic and runs at 26fps. We use a 1D linear convolutional network to directly infer the rigid moving least squares warping which implicitly balances between the global rigidity and local flexibility. We also collect a selfie video dataset with 1005 videos for evaluation.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary
MP4
Code+Data
|

|
Neural Reflectance Fields for Appearance Acquisition
arXiv 2020
We present Neural Reflectance Fields, a novel deep scene representation that encodes volume density, normal and reflectance properties at any 3D point in a scene using a fully-connected neural network. We combine this representation with a physically-based differentiable ray marching framework that can render images from a neural reflectance field under any viewpoint and light. We demonstrate that neural reflectance fields can be estimated from images captured with a simple collocated camera-light setup.
Paper: PDF MP4
|

|
Fourier Features Let Networks Learn High Frequency Functions in Low Dimensional Domains
NeurIPS 2020
We show that passing input points through a simple Fourier feature mapping enables a multilayer perceptron (MLP) to learn high-frequency functions in low-dimensional problem domains. These results shed light on recent advances in computer vision and graphics that achieve state-of-the-art results by using MLPs for complex 3D objects and scenes.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Light Stage Super-Resolution: Continuous High-Frequency Relighting
SIGGRAPH Asia 2020
This paper proposes a learning-based solution for the super-resolution of scans of human faces taken from a light stage. Given an arbitrary query light direction, our method aggregates the captured images corresponding to neighboring lights in the stage, and uses a neural network to synthesize a rendering of the face that appears to be illuminated by a virtual light source at the query location.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4
|

|
Analytic Spherical Harmonic Gradients for Real-Time Rendering with Many Polygonal Area Lights
SIGGRAPH 2020
In this paper, we develop a novel analytic formula for the spatial gradients of the spherical harmonic coefficients for uniform polygonal area lights. The result is a significant generalization, involving the Reynolds transport theorem to reduce the problem to a boundary integral for which we derive a new analytic formula.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4
|

|
NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
(Best Paper Honorable Mention)
ECCV 2020
We synthesize novel views of complex scenes by optimizing an underlying continuous volumetric scene function using a sparse set of input views. Our algorithm represents a scene using a fully-connected (non-convolutional) deep network whose input is a single continuous 5D coordinate. We use classic differentiable volume rendering to create images from this representation.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4 YouTube
|

|
Deep Reflectance Volumes: Relightable Reconstructions from Multi-View Photometric Images
ECCV 2020
We develop a novel volumetric scene representation for reconstruction from unstructured images. Our representation consists of opacity, surface normal and reflectance voxel grids. We present a novel physically-based differentiable volume ray marching framework to render these scene volumes under arbitrary viewpoint and lighting.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4
|

|
Deep Multi Depth Panoramas for View Synthesis
ECCV 2020
We propose a learning-based approach for novel view synthesis for multi-camera 360 degree panorama capture rigs. We present a novel scene representation, Multi Depth Panorama (MDP), that consists of multiple RGBD alpha panoramas that represent both scene geometry and appearance.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4
|

|
Deep Kernel Density Estimation for Photon Mapping
EGSR 2020
We present a novel learning-based photon mapping method that can be used to synthesize photrealistic images with detailed caustics from very sparse photons for scenes with complex diffuse-specular interactions. This is the first deep learning method for denoising particle-based rendering, and can produce global illumination effects like caustics with an order of magnitude fewer photons compared to previous photon mapping methods.
Paper: PDF
|

|
3D Mesh Processing using GAMer 2 to enable reaction-diffusion simulations in realistic cellular geometries
PLOS Computational Biology 2020
Recent advances in electron microscopy have enabled the imaging of
single cells in 3D at nanometer length scale resolutions. An uncharted
frontier for in silico biology is the ability to simulate cellular
processes using these observed geometries. In this paper, we describe
the use of our recently rewritten mesh processing software, GAMer 2,
to bridge the gap between poorly conditioned meshes generated from
segmented micrographs and boundary marked tetrahedral meshes which are
compatible with simulation.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Inverse Rendering for Complex Indoor Scenes: Shape, Spatially-Varying Lighting
and SVBRDF from a Single Image
CVPR 2020
We propose a deep inverse rendering framework for indoor scenes. From a single RGB image of an arbitrary indoor scene, we obtain a complete scene reconstruction, estimating shape, spatially-varying lighting, and spatially-varying, non-Lambertian surface reflectance. Our novel inverse rendering network incorporates physical insights.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Deep Stereo using Adaptive Thin Volume Representation with Uncertainty Awareness
CVPR 2020
We present Uncertainty-aware Cascaded Stereo Network (UCS-Net) for 3D reconstruction from multiple RGB images. We propose adaptive thin volumes (ATVs) for multi-view stereo (MVS). In an ATV, the depth hypothesis of each plane is spatially-varying, which adapts to the uncertainties of previous per-pixel depth predictions.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Learning Video Stabilization Using Optical Flow
CVPR 2020
We propose a novel neural network that infers the per-pixel warp fields for video stabilization from the optical flow fields of the input video. We also propose a pipeline that uses optical flow principal components for motion inpainting and warp field smoothing. Our method gives a 3x speed improvement compared to previous optimization methods.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4
|

|
Deep 3D Capture: Geometry and Reflectance from Sparse Multi-View Images
CVPR 2020
We introduce a novel learning-based method to reconstruct the high-quality geometry and complex, spatially-varying BRDF of an arbitrary object from a sparse set of only six images captured by wide-baseline cameras under collocated point lighting. We construct high-quality geometry and per-vertex BRDFs.
Paper: PDF Video: MP4
|

|
Deep Recurrent Network for Fast and Full-Resolution Light Field Deblurring
Sig. Proc. Letters 2019
We propose a novel light field recurrent deblurring network that is trained under 6 degree-of-freedom camera motion-blur model. By combining the real light field captured using Lytro Illum and synthetic light field rendering of 3D scenes from UnrealCV, we provide a large-scale blurry light field dataset to train the network.
Paper: PDF
|

|
A Differential Theory of Radiative Transfer
SIGGRAPH Asia 2019
We introduce a differential theory of radiative transfer, which
shows how individual components of the radiative transfer equation
(RTE) can be differentiated with respect to arbitrary differentiable
changes of a scene. Our theory encompasses the same generality as the
standard RTE, allowing differentiation while accurately handling a
large range of light transport phenomena such as volumetric absorption
and scattering, anisotropic phase functions, and heterogeneity.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Learning Generative Models for Rendering Specular Microgeometry
SIGGRAPH Asia 2019
Rendering specular material appearance is a core problem of
computer graphics. We propose a novel direction: learning the
high-frequency directional patterns from synthetic or measured
examples, by training a generative adversarial network (GAN). A key
challenge in applying GAN synthesis to spatially-varying BRDFs is
evaluating the reflectance for a single location and direction without
the cost of evaluating the whole hemisphere. We resolve this using a
novel method for partial evaluation of the generator network.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Deep CG2Real: Synthetic-to-Real Translation via Image Disentanglement
ICCV 2019
We present a method to improve the visual realism of low-quality,
synthetic images, e.g. OpenGL renderings. Training an unpaired
synthetic-to-real translation network in image space is severely
under-constrained and produces visible artifacts. Instead, we propose
a semi-supervised approach that operates on the disentangled shading
and albedo layers of the image. Our two-stage pipeline first learns to
predict accurate shading in a supervised fashion using physically-based
renderings as targets, and further increases the realism of the
textures and shading with an improved CycleGAN network.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Selfie Video Stabilization
PAMI 2019
We propose a novel algorithm for stabilizing selfie videos. Our goal
is to automatically generate stabilized video that hasoptimal smooth
motion in the sense of both foreground and background. The key insight
is that non-rigid foreground motion in selfievideos can be analyzed
using a 3D face model, and background motion can be analyzed using
optical flow.
Paper: PDF
Video (ECCV 18): MP4
|

|
Deep View Synthesis from Sparse Photometric Images
SIGGRAPH 2019
In this paper, we synthesize novel viewpoints across a wide range of
viewing directions (covering a 60 degree cone) from a sparse set of
just six viewing directions. Our method is based on a deep
convolutional network trained to directly synthesize new views from the
six input views. This network combines 3D convolutions on a plane
sweep volume with a novel per-view per-depth plane attention map
prediction network to effectively aggregate multi-view appearance.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
Video: MOV
|

|
Local Light Field Fusion: Practical View Synthesis with Prescriptive Sampling Guidelines
SIGGRAPH 2019
We present a practical and robust deep learning solution for capturing
and rendering novel views of complex real world scenes for virtual
exploration. We propose an algorithm for view synthesis from an
irregular grid of sampled views that first expands each sampled view
into a local light field via a multiplane image (MPI)
scene representation, then renders novel views by blending adjacent
local lightfields. We extend traditional plenoptic sampling theory to
derive a bound that specifies precisely how densely users should sample
views of a given scene when using our algorithm.
Paper: PDF
Video: YouTube
Code: Project
|

|
Accurate Appearance Preserving Filtering for Rendering Displacement-Mapped Surfaces
SIGGRAPH 2019
In this paper, we introduce a new method that prefilters displacement
maps and BRDFs jointly and constructs SVBRDFs at reduced
resolutions. These SVBRDFs preserve the appearance of the input models
by capturing both shadowing-masking and interreflection effects.
Further, we show that the 6D scaling function can be factorized into a
2D function of surface location and a 4D function of direction. By
exploiting the smoothness of these functions, we develop a simple and
efficient factorization method that does not require computing the full
scaling function.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
Slides: PPTX
Code and Data: ZIP
|

|
Single Image Portrait Relighting
SIGGRAPH 2019
We present a system for portrait relighting: a neural network that
takes as input a single RGB image of a portrait taken with a standard
cellphone camera in an unconstrained environment, and from that image
produces a relit image of that subject as though it were illuminated
according to any provided environment map.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
Video: M4V
|

|
Pushing the Boundaries of View Extrapolation with Multiplane Images
CVPR 2019 Best Paper Finalist
We present a theoretical analysis showing how the range of views that
can be rendered from a multi-plane image (MPI) increases linearly with
the MPI disparity sampling frequency, as well as a novel MPI
prediction procedure that theoretically enables view extrapolations of
up to 4x the lateral viewpoint movement allowed by prior work.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
YouTube: Link With Appendices: PDF
|

|
Robust Video Stabilization by Optimization in CNN Weight Space
CVPR 2019
We directly model the appearance change as
the dense optical flow field of consecutive frames, which leads to a
large scale non-convex problem. By solving the problem in the CNN
weight space rather than directly for image pixels, we make it a
viable formulation for video stabilization. Our method trains the CNN
from scratch on each specific input example, and intentionally
overfits to produce the best result.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Deep HDR Video from Sequences with Alternating Exposures
Eurographics 2019
A practical way to generate a high dynamic range (HDR) video using
off-the-shelf cameras is to capture a sequence with alternating
exposures and reconstruct the missing content at each
frame. Unfortunately, existing approaches are typically slow and are
not able to handle challenging cases. In this paper, we propose a
learning-based approach to address this difficult problem. To do this,
we use two sequential convolutional neural networks (CNN) to model the
entire HDR video reconstruction process.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Analysis of Sample Correlations for Monte Carlo Rendering
Eurographics 2019
Monte Carlo integrators sample the integrand at specific sample point locations. The distribution of these sample points determines convergence rate and noise in the final renderings. The characteristics of such distributions can be uniquely represented in terms of correlations of sampling point locations. We aim to provide a comprehensible and accessible overview of techniques developed over the last decade to analyze such correlations.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Connecting Measured BRDFs to Analytic BRDFs by Data-Driven Diffuse-Specular Separation
SIGGRAPH Asia 2018
We propose a novel framework for connecting measured and analytic
BRDFs, by separating a measured BRDF into diffuse and specular
components. This enables measured BRDF editing, a compact measured
BRDF model, and insights in relating measured and analytic BRDFs. We
also design a robust analytic fitting algorithm for two-lobe
materials.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Learning to Reconstruct Shape and Spatially-Varying Reflectance from a
Single Image
SIGGRAPH Asia 2018
We demonstrate that we can recover non-Lambertian, spatially-varying BRDFs
and complex geometry belonging to any arbitrary shape class, from a
single RGB image captured under a combination of unknown environment
illumination and flash lighting. We achieve this by training a deep
neural network to regress shape and reflectance from the image. We
incorporate an in-network rendering layer that includes global illumination.
Paper: PDF
Video: MOV
Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Height-from-Polarisation with Unknown Lighting or Albedo
PAMI Aug 2018
We present a method for estimating surface height directly from a
single polarisation image simply by solving a large, sparse system of
linear equations. Our method is applicable to dielectric objects exhibiting
diffuse and specular reflectance, though lighting and albedo must be known.
We relax this requirement by showing that either spatially varying albedo or
illumination can be estimated from the polarisation image alone using
nonlinear methods. We believe that our method is the first passive, monocular
shape-from-x technique that enables well-posed height estimation with
only a single, uncalibrated illumination condition.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Selfie Video Stabilization
ECCV 2018
We propose a novel algorithm for stabilizing selfie videos. Our goal
is to automatically generate stabilized video that has optimal smooth
motion in the sense of both foreground and background. The key insight
is that non-rigid foreground motion in selfie videos can be analyzed
using a 3D face model, and background motion can be analyzed using
optical flow.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
|

|
Rendering Specular Microgeometry with Wave Optics
SIGGRAPH 2018
We design the first rendering algorithm based on a wave optics model,
but also able to compute spatially-varying specular highlights with
high-resolution detail. We compute a wave optics reflection integral
over the coherence area; our solution is based on approximating the
phase-delay grating representation of a micron-resolution surface
heightfield using Gabor kernels. Our results show both
single-wavelength and spectral solution to reflection from common
everyday objects, such as brushed, scratched and bumpy metals.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
Supplementary: Supplementary
|

|
Deep Image-Based Relighting from Optimal Sparse Samples
SIGGRAPH 2018
We present an image-based relighting method that can synthesize scene
appearance under novel, distant illumination from the visible
hemisphere, from only five images captured under pre-defined
directional lights. We show that by combining a custom-designed
sampling network with the relighting network, we can jointly learn
both the optimal input light directions and the relighting function.
Paper: PDF
Video: MOV
Project: Code, Data
|

|
Analytic Spherical Harmonic Coefficients for Polygonal Area Lights
SIGGRAPH 2018
We present an efficient closed-form solution for projection of uniform
polygonal area lights to spherical harmonic coefficients of arbitrary
order, enabling easy adoption of accurate area lighting in PRT systems,
with no modifications required to the core PRT framework. Our method
only requires computing zonal harmonic (ZH) coefficients, for which we
introduce a novel recurrence relation.
Paper: PDF
Video: MOV
Project: Code, Data
|

|
Deep Adaptive Sampling for Low Sample Count Rendering
EGSR 2018
Recently, deep learning approaches have proven successful at removing
noise from Monte Carlo (MC) rendered images at extremely low sampling
rates, e.g., 1-4 samples per pixel (spp). While these methods provide
dramatic speedups, they operate on uniformly sampled MC rendered
images. We address this issue by proposing a deep learning
approach for joint adaptive sampling and reconstruction of MC rendered
images with extremely low sample counts.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Deep Hybrid Real and Synthetic Training for Intrinsic Decomposition
EGSR 2018
Intrinsic image decomposition is the process of separating the
reflectance and shading layers of an image. In this paper, we propose
to systematically address this problem using a deep convolutional
neural network (CNN). In addition to directly supervising the network
using synthetic images, we train the network by enforcing it to
produce the same reflectance for a pair of images of the same
real-world scene with different illuminations. Furthermore, we improve
the results by incorporating a bilateral solver layer into our system
during both training and test stages.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Image to Image Translation for Domain Adaptation
CVPR 2018
We propose a general framework for unsupervised domain adaptation,
which allows deep neural networks trained on a source domain to be
tested on a different target domain without requiring any training
annotations in the target domain. We apply our method for domain
adaptation between MNIST, USPS, and SVHN datasets, and Amazon, Webcam
and DSLR Office datasets in classification tasks, and also between
GTA5 and Cityscapes datasets for a segmentation task. We demonstrate
state of the art performance on each of these datasets.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Learning to See through Turbulent Water
WACV 2018
This paper proposes training a deep convolution neural network to
undistort dynamic refractive effects using only a single image.
Unlike prior works on
water undistortion, our method is trained end-to-end, only requires a
single image and does not use a ground truth template at test time.
Paper: PDF
Project: Code/Data
|

|
A BSSRDF Model for
Efficient Rendering of Fur with Global Illumination
SIGGRAPH Asia 2017
We present the first global illumination model, based on dipole
diffusion for subsurface scattering, to approximate light bouncing
between individual fur fibers. We model complex light and fur
interactions as subsurface scattering, and use a simple neural network
to convert from fur fibers' properties to scattering parameters.
Paper: PDF
Video: QT
|

|
Learning to Synthesize a 4D RGBD Light Field from a Single Image
ICCV 2017
We present a machine learning algorithm that takes as input a 2D RGB
image and synthesizes a 4D RGBD light field (color and depth of the
scene in each ray direction). For training, we introduce the largest
public light field dataset, consisting of over 3300 plenoptic camera
light fields of scenes containing flowers and plants.
Paper: PDF
Video: MPEG
Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Linear Differential Constraints for Photo-polarimetric Height Estimation
ICCV 2017
In this paper we present a differential approach to photo-polarimetric
shape estimation. We propose several alternative differential
constraints based on polarisation and photometric shading information
and show how to express them in a unified partial differential
system. Our method uses the image ratios technique to combine shading
and polarisation information in order to directly reconstruct surface
height, without first computing surface normal vectors.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Depth and Image Restoration from Light Field in a Scattering Medium
ICCV 2017
Traditional imaging methods and computer vision algorithms are often
ineffective when images are acquired in scattering media, such as
underwater, fog, and biological tissue. Here, we explore the use of
light field imaging and algorithms for image restoration and depth
estimation that address the image degradation from the medium.
We propose shearing and refocusing multiple views of the light field
to recovera single image of higher quality than what is possible from a
single view. We demonstrate the benefits of our method through
extensive experimental results in a water tank.
Paper: PDF
|

|
An Efficient and Practical Near and Far Field Fur Reflectance Model
SIGGRAPH 2017
We derive a compact BCSDF model for fur reflectance with only 5
lobes. Our model unifies hair and fur rendering, making it easy to
implement within standard hair rendering software. By exploiting
piecewise analytic integration, our method further enables a
multi-scale rendering scheme that transitions between near and
far-field rendering smoothly and efficiently for the first time.
Paper: PDF
Video: QT
Papers Trailer: Video
|

|
Light Field Video Capture Using a Learning-Based Hybrid Imaging System
SIGGRAPH 2017
We develop a hybrid imaging system, adding a standard video camera to
a light field camera to capture the temporal information. Given a 3
fps light field sequence and a standard 30 fps 2D video, our system
can then generate a full light field video at 30 fps. We adopt a
learning-based approach, which can be decomposed into two steps:
spatio-temporal flow estimation and appearance estimation,
enabling consumer light field videography.
Paper: PDF
Video: MPEG
Code/Data: Project
|

|
Patch-Based Optimization for Image-Based Texture Mapping
SIGGRAPH 2017
Image-based texture mapping is a common way of producing texture
mapsfor geometric models of real-world objects. We propose a novel
global patchbasedoptimization system to synthesize the aligned
images. Specifically, weuse patch-based synthesis to reconstruct a set
of photometrically-consistent aligned images by drawing information
from the source images. Our optimization system is simple, flexible,
and more suitable for correcting large misalignments than other
techniques such as local warping.
Paper: PDF
Video: MPEG
Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Deep High Dynamic Range Imaging of Dynamic Scenes
SIGGRAPH 2017
Producing a high dynamic range (HDR) image from a set of images with
different exposures is a challenging process for dynamic scenes.
We use a convolutional neural network (CNN) as our learning model and
present and compare three different system architectures to model the
HDR merge process. Furthermore, we create a large dataset of input LDR
images and their corresponding ground truth HDR images to train our
system.
Paper: PDF
Project Page: Code/Data
|

|
Light Field Blind Motion Deblurring
CVPR 2017
By analyzing the motion-blurred light field in
the primal and Fourier domains, we develop intuition into the effects
of camera motion on the light field, show the advantages of capturing
a 4D light field instead of a conventional 2D image for
motion deblurring, and derive simple methods of motion deblurring in
certain cases. We then present an algorithm to blindly deblur light
fields of general scenes without any estimation ofscene geometry.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Robust Energy Minimization for BRDF-Invariant Shape from Light Fields
CVPR 2017
We present a variational energy minimization framework for robust
recovery of shape in multiview stereo with complex, unknown BRDFs. While
our formulation is general, we demonstrate its efficacy on shape
recovery using a single light field image, where the microlens array
may be considered as a realization of a purely translational multiview
stereo setup. Our formulation automatically balances contributions from
texture gradients, traditional Lambertian photoconsistency,
an appropriate BRDF-invariant PDE and a smoothness prior.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary
|

|
Gradient-Domain Vertex Connection and Merging
EGSR 2017
We present gradient-domain vertex connection and merging (G-VCM), a new
gradient-domain technique motivated by primal domain VCM. Our method
enables robust gradient sampling in the presence of complex transport,
such as specular-diffuse-specular paths, while retaining the denoising
power and fast convergence of gradient-domain bidirectional path
tracing.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Multiple Axis-Aligned Filters for Rendering of Combined Distribution Effects
EGSR 2017
We present a novel filter for efficient rendering of combined effects,
involving soft shadows and depth of field, with global (diffuse
indirect) illumination. We approximate the wedge spectrum with
multiple axis-aligned filters, marrying the speed of axis-aligned
filtering with an even more accurate (compact and tighter)
representation than sheared filtering.
Paper: PDF
Video: AVI
|

|
SVBRDF-Invariant Shape and Reflectance Estimation from a Light-Field Camera
PAMI 2017
Light-field cameras have recently emerged as a powerful tool for
one-shot passive 3D shape capture. However, obtaining the shape of
glossy objects like metals or plastics remains challenging, since
standard Lambertian cues like photo-consistency cannot be easily
applied. In this paper, we derive a spatially-varying
(SV)BRDF-invariant theory for recovering 3D shape and reflectance from
light-field cameras.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Antialiasing Complex Global Illumination Effects in Path-space
TOG 2017
We present the first method to efficiently predict antialiasing
footprints to pre-filter color-, normal-, and displacement-mapped
appearance in the context of multi-bounce global illumination. We
derive Fourier spectra for radiance and importance functions that allow
us to compute spatial-angular filtering footprints at path vertices.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Learning-Based View Synthesis for Light Field Cameras
SIGGRAPH Asia 2016
we propose a novel learning-based approach to synthesize new views
from a sparse set of input views for light field cameras.
We use two sequential
convolutional neural networks to model these two components and train
both networks simultaneously by minimizing the error between the
synthesized and ground truth images.
Paper: PDF
Video: MPEG
Dataset: Project Page
|

|
Minimal BRDF Sampling for Two-Shot Near-Field Reflectance Acquisition
SIGGRAPH Asia 2016
We develop a method to acquire the BRDF of a homogeneous flat sample
from only two images, taken by a near-field perspective camera, and lit
by a directional light source. We develop a mathematical framework to
estimate error from a given set of measurements, including the use of
multiple measurements in an image simultaneously, as needed for
acquisition from near-field setups.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary: PDF
Comparison Video: QT
|

|
Downsampling Scattering Parameters for Rendering Anisotropic Media
SIGGRAPH Asia 2016
Volumetric micro-appearance models have provided remarkably high-quality
renderings, but are highly data intensive and usually require tens of
gigabytes in storage. We introduce a joint optimization of single-scattering
albedos and phase functions to accurately downsample heterogeneous and
anisotropic media.
Paper: PDF
Video: MPEG
|

|
Photometric Stereo in a Scattering Medium
PAMI 2016
Photometric stereo is widely used for 3D reconstruction. However, its
use in scattering media such as water, biologicaltissue and fog has
been limited until now, because of forward scattered light from both
the source and object, as well as light scatteredback from the medium
(backscatter). Here we make three contributions to address the key
modes of light propagation, under thecommon single scattering
assumption for dilute media.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Linear Depth Estimation from an Uncalibrated, Monocular Polarisation Image
ECCV 2016
We present a method for estimating surface height directly from a
single polarisation image simply by solving a large, sparse system of
linear equations. To do so, we show how to express
polarisation constraints as equations that are linear in the unknown
depth. Our method is applicable to objects with uniform albedo
exhibiting diffuse and specular reflectance. We believe that
our method is the first monocular, passive shape-from-x technique that
enables well-posed depth estimation with only a single, uncalibrated
illumination condition.
Paper: PDF
|

|
A 4D Light-Field Dataset and CNN Architectures for Material Recognition
ECCV 2016
We introduce a new light-field dataset of materials, and take
advantage of the recent success of deep learning to perform material
recognition on the 4D light-field. Our dataset contains 12 material
categories, each with 100 images taken with a Lytro Illum. Since
recognition networks have not been trained on 4D images before, we
propose and compare several novel CNN architectures to train on
light-field images. In our experiments, the best performing CNN
architecture achieves a 7% boost compared with 2D image classification.
Paper: PDF
HTML Comparison
dataset (2D thumbnail)
Full Dataset (16GB)
|

|
Sparse Sampling for Image-Based SVBRDF Acquisition
Material Appearance Modeling Workshop, 2016
We acquire the data-driven spatially-varying (SV)BRDF of a flat sample
from only a small number of images (typically 20). We generalize the
homogenous BRDF acquisition work of Nielsen et al., who derived an
optimal minmal set of lighting/view directions. We demonstrate our
method on SVBRDF measurements of new flat materials, showing thatfull
data-driven SVBRDF acquisition is now possible from a sparse set of
only about 20 light-view pairs.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Position-Normal Distributions for Efficient Rendering of Specular Microstructure
SIGGRAPH 2016
Specular BRDF rendering traditionally approximates surface
microstructure using a smooth normal distribution, but this ignores
glinty effects, easily observable in the real world. We treat a
specular surface as a four-dimensional position-normal distribution,
and fit this distribution using millions of 4D Gaussians, which we
call elements. This leads to closed-form solutions to the required
BRDF evaluation and sampling queries, enabling the first practical
solution to rendering specular microstructure.
Paper: PDF Video:
MP4
Press: UCSD
PhysOrg
Digital Trends
Eureka Alert
Tech Crunch
|

|
Shape Estimation from Shading, Defocus, and Correspondence Using Light-Field
Angular Coherence
PAMI 2016
We show that combining all three sources of information: defocus,
correspondence, and shading, outperforms state-of-the-art light-field
depth estimation algorithms in multiple scenarios.
Paper: PDF
|

|
SVBRDF-Invariant Shape and Reflectance Estimation from Light-Field Cameras
CVPR 2016
Light-field cameras have recently emerged as a powerful tool for one-shot passive 3D shape capture. However, obtaining the shape of glossy objects like metals, plastics or ceramics remains challenging, since standard Lambertian cues like photo-consistency cannot be easily applied. In this paper, we derive a spatially-varying (SV)BRDF-invariant theory for recovering 3D shape and reflectance from light-field cameras.
Paper: PDF
|
|
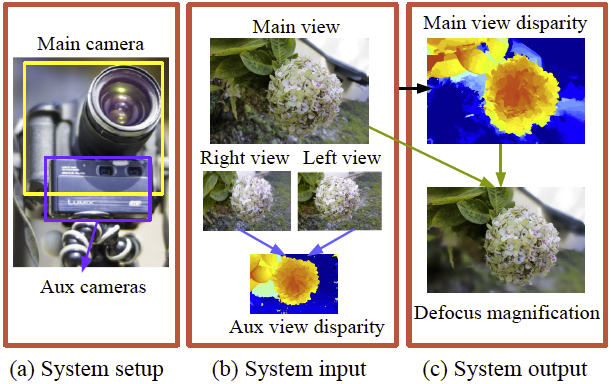
Depth from Semi-Calibrated Stereo and Defocus
CVPR 2016
In this work, we propose a multi-camera system where we combine a main
high-quality camera with two low-res auxiliary cameras. Our goal is,
given the low-res depth map from the auxiliary cameras, generate a
depth map from the viewpoint of the main camera. Ours is a
semi-calibrated system, where the auxiliary stereo cameras are
calibrated, but the main camera has an interchangeable lens, and is
not calibrated beforehand.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Depth Estimation with Occlusion Modeling Using Light-field Cameras
PAMI 2016
In this paper, an occlusion-aware depth estimation algorithm is
developed; the method also enables identification of occlusion
edges,which may be useful in other applications. It can be shown that
although photo-consistency is not preserved for pixels at occlusions,
it still holds in approximately half the viewpoints. Moreover, the line
separating the two view regions (occluded object vs. occluder) has
the same orientation as that of the occlusion edge in the spatial
domain. By ensuring photo-consistency in only the occluded view
region, depth estimation can be improved.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Fast 4D Sheared Filtering for Interactive Rendering of Distribution Effects
ACM Trans. Graphics Dec 2015
We present a new approach for fast sheared filtering on the GPU. Our
algorithm factors the 4D sheared filter into four 1D filters. We derive
complexity bounds for our method, showing that the per-pixel complexity
is reduced from O(n^2 l^2) to O(nl), where n is the linear filter width
(filter size is O(n^2)) and l is the (usually very small) number of
samples for each dimension of the light or lens per pixel (spp is
l2). We thus reduce sheared filtering overhead dramatically.
Paper: PDF
Video: MPEG
|

|
Physically-Accurate Fur Reflectance: Modeling, Measurement and Rendering
SIGGRAPH Asia 2015
In this paper, we develop a physically-accurate reflectance model for
fur fibers. Based on anatomical literature and measurements, we develop
a double cylinder model for the reflectance of a single fur fiber,
where an outer cylinder represents the biological observation of a
cortex covered by multiple cuticle layers, and an inner cylinder
represents the scattering interior structure known as the medulla.
Paper: PDF
MS thesis of Chiwei Tseng
Data
|
|
Anisotropic Gaussian Mutations for Metropolis Light Transport through
Hessian-Hamiltonian Dynamics
SIGGRAPH Asia 2015
We present a Markov Chain Monte Carlo(MCMC) rendering algorithm that
extends Metropolis Light Transport by automatically and explicitly
adapting to the local shape of the integrand, thereby increasing the
acceptance rate. Our algorithm characterizes the local behavior of
throughput in path space using its gradient as well as its Hessian. In
particular, the Hessian is able to capture the strong anisotropy of the
integrand.
Paper: PDF
|

|
On Optimal, Minimal BRDF Sampling for Reflectance Acquisition
SIGGRAPH Asia 2015
In this paper, we address the problem of reconstructing a measured BRDF
from a limited number of samples. We present a novel mapping of the
BRDF space, allowing for extraction of descriptive principal components
from measured databases, such as the MERL BRDF database. We optimize
for the best sampling directions, and explicitly provide the optimal
set of incident and outgoing directions in the Rusinkiewicz
parameterizationfor n = 1; 2; 5; 10; 20 samples. Based on the
principal components, we describe a method for accurately
reconstructing BRDF data from these limited sets of samples.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Photometric Stereo in a Scattering Medium
ICCV 2015
Photometric stereo is widely used for 3D reconstruction. However, its
use in scattering media such as water, biological tissue and fog has
been limited until now, because of forward scattered light from both
the source and object, as well as light scattered back from the medium
(backscatter). Here we make three contributions to address the key
modes of light propagation, under the common single
scattering assumption for dilute media.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Occlusion-aware Depth Estimation Using Light-field Cameras
ICCV 2015
In this paper, we develop a depth estimation algorithm for light field
cameras that treats occlusion explicitly; the method also
enables identification of occlusion edges, which may be useful in other
applications. We show that, although pixels at occlusions do not
preserve photo-consistency in general, they are still consistent in
approximately half the viewpoints.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Oriented Light-Field Windows for Scene Flow
ICCV 2015
For Lambertian surfaces focused to the correct depth, the 2D
distribution of angular rays from a pixel remains consistent. We build
on this idea to develop an oriented 4D light-field window that accounts
for shearing(depth), translation (matching), and windowing. Our
main application is to scene flow, a generalization of optical flow to
the 3D vector field describing the motion of each point in the scene.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Depth Estimation and Specular Removal for Glossy Surfaces Using Point and Line Consistency with Light-Field Cameras
PAMI 2015 (to appear)
Light-field cameras have now become available in both consumer and
industrial applications, and recent papers havedemonstrated practical
algorithms for depth recovery from a passive single-shot
capture. However, current light-field depth estimationmethods are
designed for Lambertian objects and fail or degrade for glossy or
specular surfaces. In this paper, wepresent a novel theory of the
relationship between light-field data and reflectance from the
dichromatic model.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Depth from Shading, Defocus, and Correspondence Using Light-Field Angular Coherence
CVPR 2015
Using shading information is essential to improve shape estimation
from light field cameras. We develop an improved technique for local
shape estimation from defocus and correspondence cues, and show how
shading can be used to further refine the depth. We show that the angular
pixels have angular coherence, which exhibits three properties: photoconsistency, depth consistency, and shading consistency.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Probabilistic Connections for Bidirectional Path Tracing
Computer Graphics Forum (EGSR) 2015
Bidirectional path tracing (BDPT) with Multiple Importance Sampling is
one of the most versatile unbiased rendering algorithms today. BDPT
repeatedly generates sub-paths from the eye and the lights, which are
connected for each pixel and then discarded. Unfortunately, many such
bidirectional connections turn out to have low contribution to the
solution. Our key observation is that we can importance sample
connections to an eye sub-path by considering multiple light sub-paths
at once and creating connections probabilistically.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Filtering Environment Illumination for Interactive Physically-Based Rendering in Mixed Reality
EGSR 2015
We propose accurate filtering of a noisy Monte-Carlo image using
Fourier analysis. Our novel analysis extends previous works by showing
that the shape of illumination spectra is not always a line or wedge,
as in previous approximations, but rather an ellipsoid. Our primary
contribution is an axis-aligned filtering scheme that preserves the
frequency content of the illumination.We also propose a novel
application of our technique to mixed reality scenes, in which virtual
objects are inserted into a real video stream so as to become
indistinguishable from the real objects.
Paper: PDF
Video: MP4
Supplementary: PDF
|

|
Recent Advances in Adaptive Sampling and Reconstruction for Monte Carlo Rendering
EUROGRAPHICS 2015
In this paper we survey recent
advances in adaptive sampling and reconstruction. We distinguish between a priori
methods that analyze the light transport equations and derive sampling
rates and reconstruction filters from this analysis, and a posteriori
methods that apply statistical techniques to sets of samples.
Paper: PDF
|

|
A Light Transport Framework for Lenslet Light Field Cameras
ACM Transactions on Graphics (Apr 2015).
It is often stated that there is a fundamental tradeoff
between spatial and angular resolution of lenslet light field cameras,
but there has been limited
understanding of this tradeoff theoretically or numerically.
In this paper, we
develop a light transport framework for understanding the fundamental
limits of light field camera resolution.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary Images: PDF
|

|
City Forensics: Using Visual Elements to Predict Non-Visual City Attributes
IEEE TVCG [SciVis 2014]. Honorable Mention for Best Paper Award
We present a method for automatically identifying and validating
predictive relationships between the visual appearance of a city and
its non-visual attributes (e.g. crime statistics, housing prices,
population density etc.). We also test human performance for
predicting theft based on street-level images and show that our
predictor outperforms this baseline with 33% higher accuracy on average.
Paper: PDF
|

|
High-Order Similarity Relations in Radiative Transfer
SIGGRAPH 2014.
Radiative transfer equations (RTEs) with different scattering
parameters can lead to identical solution radiance fields. Similarity
theory studies this effect by introducing a hierarchy of equivalence
relations called similarity relations. Unfortunately, given a set of
scattering parameters, it remains unclear how to find altered ones
satisfying these relations, significantly limiting the theory's
practical value. This paper presents a complete exposition of
similarity theory, which provides fundamental insights into the
structure of the RTE's parameter space. To utilize the theory in its
general high-order form, we introduce a new approach to solve for the
altered parameters including the absorption and scattering
coefficients as well as a fully tabulated phase function.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
Rendering Glints on High-Resolution Normal-Mapped Specular Surfaces
SIGGRAPH 2014.
Complex specular surfaces under sharp point lighting show a
fascinating glinty appearance, but rendering it is an unsolved
problem. Using Monte Carlo pixel sampling for this purpose is
impractical: the energy is concentrated in tiny highlights that take up
a minuscule fraction of the pixel. We instead compute an accurate
solution using a completely different deterministic approach.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
Factored Axis-Aligned Filtering for Rendering Multiple Distribution Effects
SIGGRAPH 2014.
We propose an approach to adaptively sample and filter for
simultaneously rendering primary (defocus blur) and secondary
(soft shadows and indirect illumination) distribution effects, based on
a multi-dimensional frequency analysis of the direct and indirect
illumination light fields, and factoring texture and irradiance.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
Discrete Stochastic Microfacet Models
SIGGRAPH 2014.
This paper investigates rendering glittery surfaces, ones which
exhibitshifting random patterns of glints as the surface or
viewermoves. It applies both to dramatically glittery surfaces that
containmirror-like flakes and also to rough surfaces that exhibit more
subtlesmall scale glitter, without which most glossy surfaces
appeartoo smooth in close-up. Inthis paper we present a stochastic
model for the effects of randomsubpixel structures that generates
glitter and spatial noise that behavecorrectly under different
illumination conditions and viewingdistances, while also being
temporally coherent so that they lookright in motion.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
Depth Estimation for Glossy Surfaces with Light-Field Cameras
ECCV 14 Workshop Light Fields Computer Vision.
Light-field cameras have now become available in both consumer
and industrial applications, and recent papers have demonstrated
practical algorithms for depth recovery from a passive single-shot
capture. In this paper, we develop an iterative approach to use the
benefits of light-field data to estimate and remove the specular
component, improving the depth estimation. The approach enables
light-field data depth estimation to support both specular and diffuse
scenes.
Paper: PDF
|

|
User-Assisted Video Stabilization
EGSR 2014.
We present a user-assisted video stabilization algorithm that is able
to stabilize challenging videos. First, we cluster
tracks and visualize them on the warped video. The user ensures that
appropriate tracks are selected by clicking on track clusters to
include or exclude them. Second, the user can directly specify how
regions in the output video should look by drawing quadrilaterals to
select and deform parts of the frame.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
Depth from Combining Defocus and Correspondence Using Light-Field Cameras
ICCV 2013.
Light-field cameras have recently become available to the consumer
market. An array of micro-lenses captures enough information that one
can refocus images after acquisition, as well as shift one's viewpoint
within the sub-apertures of the main lens, effectively obtaining
multiple views. Thus, depth cues from both defocus and
correspondence are available simultaneously in a single capture, and we show
how to exploit both by analyzing the EPI.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
External mask based depth and light field camera
ICCV 13 Workshop Consumer Depth Cameras for Vision.
We present a method to convert a digital single-lens reflex (DSLR)
camera into a high-resolution consumer depth and light-field camera by
affixing an external aperture mask to the main lens. Compared to the
existing consumer depth and light field cameras, our camera is easy to
construct with minimal additional costs, and our design is camera and
lens agnostic. The main advantage of our design is the ease of switching
between an SLR camera and a native resolution depth/light field
camera. We also do not need to modify the internals
of the camera or the lens.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
Axis-Aligned Filtering for Interactive Physically-Based Diffuse Indirect
Lighting
SIGGRAPH 2013.
We introduce an algorithm for interactive rendering of
physically-based global illumination, based on a novel frequency
analysis of indirect lighting. Our method combines adaptive sampling
byMonte Carlo ray or path tracing, using a standard
GPU-accelerated raytracer, with real-time reconstruction of the
resulting noisy images.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
Modular Flux Transfer: Efficient Rendering of High-Resolution Volumes with
Repeated Structures
SIGGRAPH 2013.
Common volumetric materials (fabrics, finished wood, synthesized solid
textures) are structured, with repeated patterns approximated by
tiling a small number of exemplar blocks. In this paper, we introduce
a precomputation-based rendering approach for such volumetric media
with repeated structures based on a modular transfer formulation. We
model each exemplar block as a voxel grid and precompute
voxel-to-voxel, patch-to-patch, and patch-to-voxel flux transfer matrices.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
What Object Motion Reveals About Shape with Unknown BRDF and Lighting
CVPR 2013.
We present a theory that addresses the problem of determining shape
from the (small or differential) motion of an object with unknown
isotropic reflectance, under arbitrary unknown distant illumination,
for both orthographic and perpsective projection. Our theory imposes
fundamental limits on the hardness of surface reconstruction,
independent of the method involved. Under orthographic projection, we
prove that three differential motions suffice to yield an invariant that
relates shape to image derivatives, regardless of BRDF and
illumination. Under perspective projection, we show that four
differential motions suffice to yield depth and a linear constraint on
the surface gradient.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Automatic Cinemagraph Portraits
EGSR 2013.
Cinemagraphs are a popular new type of visual media that lie
in-between photos and video; some parts of the frame are animated and
loop seamlessly, while other parts of the frame remain completely
still. Cinemagraphs are especially effective for portraits because they
capture the nuances of our dynamic facial expressions. We present a
completely automatic algorithm for generating portrait cinemagraphs
from a short video captured with a hand-held camera.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
Interactive Albedo Editing in Path-Traced Volumetric Materials
TOG 2013 (April Cover Image).
In this paper, we develop an editing algorithm that enables a material
designer to set the local (single-scattering) albedo coefficients
interactively, and see an immediate update of the emergent appearance
in the image. We also extend the technique to editing the overall mean
free path of the material. This is a difficult problem, since the function from
materials to pixel values is neither linear nor low-order polynomial.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
|

|
Gloss Perception in Painterly and Cartoon Rendering
TOG 2013.
We describe the first study of material perception in stylized images
(specifically painting and cartoon) and use non-photorealistic rendering
algorithms to evaluate how such stylization alters the perception of gloss.
This mapping allows users of NPR algorithms to predict, and correct for,
the perception of gloss in their images.
Paper: PDF
|


|
Sharpening Out of Focus Images using High-Frequency Transfer
EuroGraphics 2013.
We propose a new method to
sharpen out-of-focus images, that uses a similar but different
assisting sharp image provided by the user (such as multiple images of
the same subject in different positions captured using a burst of
photographs). We demonstrate sharpened results on out-of-focus images
in macro, sports, portrait and wildlife photography.
Paper: PDF
Video (MPEG)
Supplementary HTML
|

|
On Differential Photometric Reconstruction for Unknown, Isotropic BRDFs
PAMI 2013.
This paper presents a comprehensive theory of photometric surface
reconstruction from image derivatives, in the presence of a general,
unknown isotropic BRDF. We derive precise topological classes up to
which the surface may be determined and specify exact priors for a
full geometric reconstruction, for both shape from shading and
photometric stereo.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Compressive Structured Light for Recovering Inhomogeneous Participating
Media PAMI 2013.
We propose a new method named compressive structured light for
recovering inhomogeneous participating media. Whereas conventional
structured light methods emit coded light patterns onto the surface of
an opaque object to establish correspondence for triangulation,
compressive structured light projects patterns into a volume of
participating medium to produce images which are integral measurements
of the volume density along the line of sight.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Axis-Aligned Filtering for Interactive Sampled Soft Shadows
Siggraph Asia 2012.
We develop a simple and efficient method for soft shadows from planar
area light sources, based on explicit occlusion calculation by
raytracing, followed by adaptive image-space filtering. Since the
method is based on Monte Carlo sampling, it is accurate. Since the
filtering is in image-space, it adds minimal overhead and can be
performed at real-time frame rates. We obtain interactive speeds,
using the Optix GPU raytracing framework. Our technical approach derives from recent work on frequency analysis and sheared pixel-light filtering for offline soft shadows. While sample counts can be reduced dramatically, the sheared filtering step is slow, adding minutes of overhead. We develop the theoretical analysis to instead consider axis-aligned filtering, deriving the sampling rates and filter sizes.
Paper:
PDF
Video (MPEG)
Source Code Chrome users
may need to open these links in a new window.
|

|
Frequency-Space Decomposition and Acquisition of Light Transport under
Spatially Varying Illumination
ECCV 2012.
We show that, under spatially varying illumination, the light
transport of diffuse scenes can be decomposed into direct, near-range
(subsurface scattering and local inter-reflections) and far range
transports (diffuse inter-reflections). We show that these three
component transports are redundant either in the spatial or the
frequency domain and can be separated using appropriate illumination
patterns, achieving a theoretical lower bound.
Paper: PDF
|

|
A Theory of Monte Carlo Visibility Sampling
ACM TOG Aug 2012.
We develop a comprehensive theoretical analysis of different sampling patterns
for Monte Carlo visibility. In particular, we show the benefits of uniform
jitter sampling over stratified in some cases, and demonstrate that it produces
the lowest variance for linear lights. Surprisingly, the best pattern depends
on the shape of the light source for area lights, with uniform jitter
preferred for circular lights and stratified for square lights.
Paper: PDF
Video: MPEG4
Talk: PPT
|

|
Selectively De-Animating Video
SIGGRAPH 2012.
We present a semi-automated technique for selectively de-animating
video to remove the large-scale motions of one or more objects so that
other motions are easier to see. Our technique enables a number of
applications such as clearer motion visualization, simpler creation of
artistic cinemagraphs (photos that include looping motions in some
regions), and new ways to edit appearance and complicated motion paths
in video by manipulating a de-animated representation.
Paper: PDF
Video: MPEG4
Teaser Video:
MPEG4
|

|
Analytic Tangent Irradiance Environment Maps for Anisotropic Surfaces
EGSR 2012.
We extend spherical harmonic irradiance maps to anisotropic surfaces,
replacing Lambertian reflectance with the diffuse term of the popular
Kajiya-Kay model. We show that the terms decay even more rapidly than for
Lambertian reflectance. Existing code for irradiance environment maps can
be trivially adapted for real-time rendering with tangent irradiance
maps. We also demonstrate an application to offline rendering of the
diffuse component of fibers, using our formula as a control variate
for Monte Carlo sampling.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Importance Sampling of Reflection from Hair Fibers
JCGT 2012 (Inaugural Article).
Hair and fur are increasingly important visual features in production
rendering, and physically-based light scattering models are now
commonly used. In this paper, we enable efficient Monte Carlo
rendering of specular reflections from hair fibers. We describe a
simple and practical importance sampling strategy for the reflection
term in the Marschner hair model. Our method has been widely used in
production for more than a year, and complete pseudocode is provided.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Real-Time Rendering of Rough Refraction
IEEE TVCG Feb 2012.
We present an algorithm to render objects made of transparent materials
with rough surfaces in real-time, under distant illumination. Rough
surfaces cause wide scattering as light enters and exits objects,
which significantly complicates the rendering of such materials. We
approximate the Bidirectional Transmittance Distribution Function
(BTDF), using spherical Gaussians. We also propose two extensions, to
support spatially-varying roughness and local lighting on thin objects.
Paper: PDF
Youtube Video (from I3D 2011)
|

|
From the Rendering Equation to Stratified Light Transport Inversion International Journal of Computer Vision, 2012
In this work, we explore a theoretical analysis of inverse light
transport, relating it to its forward counterpart, expressed in the
form of the rendering equation. We show the existence of an inverse
Neumann series, that zeroes out the corresponding physical bounces of
light, which we refer to as stratified light transport inversion. Our
practical application is to radiometric compensation, where we seek to
project patterns onto real-world surfaces, undoing the effects of
global illumination.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Practical Filtering for Efficient Ray-Traced Directional Occlusion
SIGGRAPH Asia 2011
Ambient occlusion and directional (spherical harmonic) occlusion have
become a staple of production rendering, but are expensive to compute.
We give a frequency analysis of shadow light fields using distant
illumination with a general BRDF and normal mapping, allowing us to
share ray information even among complex receivers. We also present a
new rotationally-invariant filter that easily handles samples spread
over a large angular domain. Our method can deliver 4x speed up for
scenes that are computationally bound by ray tracing costs.
Paper: PDF
Supplementary Animations AVI
|

|
Sparse Reconstruction of Visual Appearance for Computer Graphics and Vision SPIE Keynote, Wavelets and Sparsity XIV 2011
A broad range of problems in computer graphics rendering, appearance
acquisition for graphics and vision, and imaging, involve sampling,
reconstruction, and integration of high-dimensional (4D-8D) signals.
We argue that dramatically sparser sampling and reconstruction of
these signals is possible, before the full dataset is acquired or
simulated. Our key idea is to exploit the structure of the data that
often lies in lower-frequency, sparse, or low-dimensional spaces.
Paper: PDF
|

|
What an Image Reveals About Material Reflectance
ICCV 2011
We derive precise conditions under which material reflectance
properties may be estimated from a single image
of a homogeneous curved surface (canonically a sphere), lit
by a directional source. Based on the observation that light
is reflected along certain (a priori unknown) preferred directions
such as the half-angle, we propose a semiparametric
BRDF abstraction that lies between purely parametric and
purely data-driven models. While it is well-known that fitting
multi-lobe BRDFs may be ill-posed under certain conditions,
prior to this work, precise results for the well-posedness of
BRDF estimation had remained elusive.
Paper: PDF
|

|
On the Duality of Forward and Inverse Light Transport
PAMI 2011, ECCV 2010
Inverse light transport seeks to undo global illumination effects,
such as interreections, that pervade images of most scenes. This paper
presents the theoretical and computational foundations for inverse
light transport as a dual of forward rendering. We demonstrate two
practical applications, namely, separation of individual bounces of
the light transport and fast projector radiometric compensation to
display images free of global illumination artifacts in real-world
environments.
Paper: PAMI
ECCV
Tech Report
Video
|

|
Data-Driven Elastic Models for Cloth: Modeling and Measurement SIGGRAPH 2011
Cloth often has complicated nonlinear, anisotropic elastic behavior
due to its woven pattern and fiber properties. However, most current
cloth simulation techniques simply use linear and isotropic elastic
models with manually selected stiffness parameters. Such simple
simulations do not allow differentiating the behavior of distinct
cloth materials such as silk or denim, and they cannot model most
materials with fidelity to their real-world counterparts. In this
paper, we present a data-driven technique to more realistically
animate cloth. These measurements can be used in most cloth simulation
systems to create natural and realistic clothing wrinkles and shapes,
for a range of different materials.
Paper: PDF
Video
|

|
Illumination Decomposition for Material Recoloring with Consistent Interreflections SIGGRAPH 2011
Changing the color of an object is a basic image editing operation,
but a high quality result must also preserve natural shading. A common
approach is to first compute reflectance and illumination intrinsic
images. Reflectances can then be edited independently, and recomposed
with the illumination. However, manipulating only the reflectance
color does not account for diffuse interreflections, and can result in
inconsistent shading in the edited image. We propose an approach for
further decomposing illumination into direct lighting, and indirect
diffuse illumination from each material.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Frequency Analysis and Sheared Filtering for Shadow Light Fields of Complex Occluders TOG 2011
Monte Carlo ray tracing of soft shadows produced by area lighting and
intricate geometries, such as the shadows through plant leaves or
arrays of blockers, is a critical challenge. This article develops
an efficient diffuse soft shadow technique for mid to far occluders
that relies on a new 4D cache and sheared reconstruction filter.
Our analysis subsumes convolution soft
shadows for parallel planes as a special case.
Paper: PDF
Supplemental Animations
|

|
Optimizing Environment Maps for Material Depiction
EGSR 2011
We present an automated system for optimizing and synthesizing
environment maps that enhance the appearance of materials in a
scene. We first identify a set of lighting design principles for
material depiction. Each principle specifies the distinctive visual
features of a material and describes how environment maps can
emphasize those features. We express these principles as linear or
quadratic image quality metrics, and present a general optimization
framework to solve for the environment map that maximizes these
metrics. We accelerate metric evaluation using an approach dual to
precomputed radiance transfer (PRT).
Paper: PDF
Video of Quality Metric
|

|
A Theory of Differential Photometric Stereo for Unknown Isotropic BRDFs
CVPR 2011
We present a comprehensive theory of photometric surface
reconstruction from image derivatives. For unknown isotropic BRDFs, we
show that two measurements of spatial and temporal image derivatives,
under unknown light sources on a circle, suffice to determine the
surface. This result is the culmination of a series of fundamental
observations. Our theoretical results are illustrated with several
examples on synthetic and real data.
Paper: PDF
Tech Report
|

|
Real-Time Rough Refraction
I3D 2011 Best Paper Award
We present an algorithm to render objects of transparent materials
with rough surfaces in real-time, under distant illumination. Rough
surfaces cause wide scattering as light enters and exits objects,
which significantly complicates the rendering of such materials. We
approximate the Bidirectional Transmittance Distribution Function
(BTDF), using spherical Gaussians, suitable for real-time estimation
of environment lighting using pre-convolution.
Paper: PDF
Youtube Video
|

|
Multi-Resolution Isotropic Strain Limiting
SIGGRAPH Asia 2010.
In this paper we describe a fast strain-limiting method that allows
stiff, incompliant materials to be simulated efficiently. Unlike prior
approaches, which act on springs or individual strain components, this
method acts on the strain tensors in a coordinate-invariant fashion
allowing isotropic behavior. For triangulated surfaces in
three-dimensional space, we also describe a complementary
edge-angle-limiting method to limit out-of-plane bending. To
accelerate convergence, we also propose a novel multi-resolution
algorithm that enforces fitted limits at each level of a
non-conforming hierarchy.
Paper: PDF
Video
|

|
Example-Based Wrinkle Synthesis for Clothing Animation
SIGGRAPH 2010.
This paper describes a method for animating the appearance of
clothing, such as pants or a shirt, that fits closely to a figure's
body. Based on the observation that the wrinkles in close-fitting
clothing behave in a predominantly kinematic fashion, we have
developed an example-based wrinkle synthesis technique. Our method
drives wrinkle generation from the pose of the figure's kinematic
skeleton. This approach allows high quality clothing wrinkles to be
combined with a coarse cloth simulation that computes the global and
dynamic aspects of the clothing motion. Further, the combined system runs at interactive rates, making it suitable for applications where high-resolution offline simulations would not be a viable option.
Paper: PDF
Video
Papers Trailer
|

|
Sparsely Precomputing the Light Transport Matrix for Real-Time Rendering
EGSR 2010.
Precomputation-based methods have enabled real-time rendering with
natural illumination, all-frequency shadows, and global
illumination. However, a major bottleneck is the precomputation time,
that can take hours to days. While the final real-time data structures
are typically heavily compressed with clustered principal component
analysis and/or wavelets, a full light transport matrix still needs to
be precomputed for a synthetic scene, often by exhaustive sampling and
raytracing. In this paper, we show that the precomputation can be made
much more efficient by adaptive and sparse sampling of light
transport. We demonstrate
sparse sampling and precomputation 5x faster than previous methods.
Paper: PDF (if no EG DL subscription see TR)
Tech Report
Video
|

|
Adaptive Wavelet Rendering
SIGGRAPH Asia 2009.
Effects such as depth of field, area lighting, antialiasing and global
illumination require evaluating a complex high-dimensional integral at
each pixel of an image. We develop a new adaptive rendering algorithm
that greatly reduces the number of samples needed for Monte Carlo
integration. Our method renders directly into an image-space wavelet
basis. Moreover, the method introduces minimal overhead, and can be
efficiently included in an optimized ray-tracing system.
Paper: PDF (44M)
|

|
Removing Image Artifacts Due to Dirty Camera Lenses and Thin Occluders
SIGGRAPH Asia 2009.
There are often physical layers between the scene and
the imaging system. For example, the lenses of consumer digital
cameras often accumulate various types of contaminants over time
(e.g., fingerprints, dust, dirt). Also, photographs are often taken
through a layer of thin occluders (e.g., fences, meshes, window
shutters, curtains, tree branches) which partially obstruct the
scene. We show that both effects can be described by a single image
formation model, and removed from digital photographs.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Precomputation-Based Rendering
Foundations and Trends in Computer Graphics and Vision 3(4), 281-369.
Precomputation-based relighting and radiance transfer has a long
history with a spurt of renewed interest, including adoption in
commercial video games, due to recent mathematical developments and
hardware advances. In this survey, we describe the mathematical
foundations, history, current research and future directions for
precomputation-based rendering.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Frequency Analysis and Sheared Reconstruction for Rendering Motion Blur
SIGGRAPH 09.
Motion blur is crucial for high-quality rendering, but is also very
expensive. Our first contribution is a frequency analysis of
motionblurred scenes, including moving objects, specular reflections,
and shadows. We show that motion induces a shear in the frequency
domain, and that the spectrum of moving scenes is usually contained in
a wedge. This allows us to compute adaptive space-time sampling rates,
to accelerate rendering. Our second contribution is a novel sheared
reconstruction filter that is aligned to the first-order direction of
motion and enables even lower sampling rates.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Moving Gradients: A Path-Based Method for Plausible Image Interpolation
SIGGRAPH 09.
We describe a method for plausible interpolation of images, with a
wide range of applications like temporal up-sampling for smooth
playback of lower frame rate video, smooth view interpolation, and
animation of still images. We develop a novel path-based framework,
greater flexibility via transition points, new ways to handle
visibility, and Poisson reconstruction to produce smooth interpolations.
Paper: PDF
Video (QT 55M)
|

|
An Empirical BSSRDF Model
SIGGRAPH 09.
Current scattering models are tuned to the two extremes of thin media
and single scattering, or highly scattering materials modeled using
the diffusion approximation. The vast intermediate range of materials
has no efficient approximation. In this work, we simulate the full
space of BSSRDFs, analogous to work on measured BRDF databases. We
show new types of scattering behavior, fitting an analytic model and
tabulating its parameters. This allows new efficient rendering and
reflectance models for a variety of BSSRDFs.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Affine Double and Triple Product Wavelet Integrals for Rendering
ACM Transactions on Graphics 28(2), Article 14, pages 1-17, Apr 2009.
Many problems in computer graphics involve integrations of products of
functions. Double- and triple-product integrals are commonly used in
applications such as all-frequency relighting or importance sampling,
but are limited to distant illumination. In contrast, near-field
lighting from planar area lights involves an affine transform of the
source radiance at different points in space. Our main contribution is
a novel affine double- and triple-product integral theory.
Paper: PDF
Video (AVI 16M)
|

|
Compressive Light Transport Sensing
ACM Transactions on Graphics 28(1), Article 3, pages 1-18, Jan 2009.
In this article we propose a new framework for capturing light
transport data of a real scene, based on the recently developed theory
of compressive sensing for sparse signals. We develop a novel
hierarchical decoding algorithm that improves reconstruction quality
by exploiting interpixel coherency relations. Additionally, we design
new nonadaptive illumination patterns that minimize measurement noise.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Multiscale Texture Synthesis
SIGGRAPH 08, Article 51, pages 1-8.
The appearance of many textures changes dramatically with scale;
imagine zooming into the planet from outer space to see large scale
continent and ocean features, then smaller cities, forests, and
finally people and trees. By using an exemplar graph with a few small
single-scale exemplars and modifying a standard parallel synthesis
method, we develop the first multiscale texture synthesis algorithm.
Paper: PDF
Video (175M)
|

|
Light Field Transfer: Global Illumination between Real and Synthetic
Objects
SIGGRAPH 08, Article 57, pages 1-6.
By using a light field interface between real and synthetic scenes, we can
composite real and virtual objects. Moreover, we can directly simulate
multiple bounces of global illumination between them. Our method is suited
even for dynamic scenes, and does not require geometric properties or
complex image-based appearance capture of the real objects.
Paper: PDF
Video (55M)
|

|
A Precomputed Polynomial Representation for Interactive BRDF Editing with
Global Illumination ACM Transactions on Graphics
27(2), Article 13, pages 1--13. Presented at SIGGRAPH 2008.
We develop a mathematical framework and practical algorithms to edit BRDFs
with global illumination in a complex scene. A key challenge is that
light transport for multiple bounces is non-linear in the scene BRDFs.
We address this by developing a new bilinear representation of the reflection
operator, deriving a polynomial multi-bounce tensor precomputed framework, and
reducing the complexity of further bounces.
Paper: PDF
Video (7M)
|

|
A Layered, Heterogeneous Reflectance Model for Acquiring and Rendering
Human Skin SIGGRAPH Asia 2008.
We introduce a layered, heterogeneous spectral reflectance model for
human skin. The model captures the inter-scattering of light among
layers, each of which may have an independent set of spatially-varying
absorption and scattering parameters. To obtain parameters for our
model, we use a novel acquisition method that begins with
multi-spectral photographs. We create complex skin visual effects such
as veins, tattoos, rashes, and freckles.
Paper: PDF (8M)
|

|
Compressive Structured Light for Recovering Inhomogeneous Participating
Media ECCV 2008.
Recovering dynamic inhomogeneous participating media is a significant
challenge in vision and graphics. We introduce a new framework of
compressive structured light, where patterns are emitted to obtain a
line integral of the volume density at each camera pixel. The
framework of compressive sensing is then used to recover the density
from a sparse set of patterns.
Paper: PDF
Video (25M)
|

|
Searching the World's Herbaria: Visual Identification of Plant Species
ECCV 2008.
This paper describes our electronic field guide project: a
collaboration of researchers in computer vision, mobile computing and
botany (the Smithsonian Institution). We have developed a hand-held
prototype and recognition algorithms that enable users to take the
picture of a leaf and identify the species in the field. The field
guide works for Plummer's Island, the woody plants in the DC area, and
the trees of NYC's Central Park. Subsequent to this paper, Prof.
Belhumeur and collaborators developed and released
LeafSnap which is a free iPhone App for visual plant species identification.
Paper: PDF
Earlier Taxon 2006 paper (PDF)
Project Website
LeafSnap
|

|
An Analysis of the BRDF In-Out Factorization for View-Dependent Relighting
EuroGraphics Symposium on Rendering 2008.
Interactive rendering with dynamic lighting and changing view is a long
standing problem and many recent PRT methods seek to address this by a
factorization of the BRDF into incident and outgoing angles. In this paper,
we analyze this factorization theoretically using spherical harmonics, and
derive the number of terms needed based on the BRDF. One result is that a
very large number of terms (10s to 100s) are needed for specular materials.
Paper: PDF
Video (18M)
|

|
Large Ray Packets for Real-Time Whitted Ray Tracing
IEEE Symposium on Interactive Ray Tracing 2008.
Real-Time Ray Tracing going beyond primary rays and hard shadows, to
reflections and refractions, is a long-standing challenge. In this work,
we evaluate and develop new algorithms for traversal and frustum culling
with large ray packets to
get speedups of 3x-6x, enabling real-time Whitted ray tracing on commodity
hardware.
Paper: PDF
|


|
A First Order Analysis of Lighting, Shading, and Shadows
ACM Transactions on Graphics, article 2, pages 1-21, Jan 2007.
We derive a complete first order or gradient theory of lighting, reflection
and shadows, taking both spatial and angular variation of the light field
into account. The gradient is by definition a sum of terms, allowing us
to consider the relative weight of spatial and angular lighting variation,
geometric curvature and bump mapping. Moreover, we derive analytic formulas
for the gradients in soft shadow or penumbra regions, demonstrating
applications to gradient-based interpolation and sampling.
Paper: PDF
|

|
A Theory of Locally Low Dimensional Light Transport
SIGGRAPH 07, article 62, pages 1-9.
We develop a theory of locally low dimensional light
transport, to analytically derive the dimensionality of light
transport for a local patch. We analyze the eigenvalues for canonical
configurations using Szego's eigenvalue theorem. We show
mathematically that for symmetric patches of area A, the number of
basis functions for glossy reflections increases linearly with A,
while for simple cast shadows, it often increases as sqrt(A). There
are practical applications to CPCA and other PRT algorithms.
Paper: PDF
Video (30M)
|

|
Frequency Domain Normal Map Filtering
SIGGRAPH 07, article 28, pages 1-11.
Filtering is critical for representing image-based detail, such as
textures or normal maps, across a variety of scales. While mipmapping
textures is commonplace, accurate normal map filtering remains a
challenging problem because of nonlinearities in shading--we cannot
simply average nearby surface normals. In this paper, we show
analytically that normal map filtering can be formalized as a
spherical convolution of the normal distribution function (NDF) and
the BRDF, for a large class of common BRDFs such as Lambertian,
microfacet and factored measurements. Our practical algorithms
leverage a significant body of previous work that has studied
lighting-BRDF convolution. We show how spherical harmonics can be used
to filter the NDF for Lambertian and low-frequency specular BRDFs,
while spherical von Mises-Fisher distributions can be used for
high-frequency materials.
Paper: PDF
Video (103M)
Very Cool Trailer (MOV 54M)
|


|
A Theory of Frequency Domain Invariants: Spherical Harmonic Identities for BRDF/Lighting Transfer and Image Consistency
ECCV 06, vol IV, pp 41-55, PAMI 30(2), pages 197-213, Feb 2008.
We develop new mathematical results based on the spherical harmonic
convolution framework for reflection. We derive novel identities, which are
the angular frequency domain analogs to common spatial domain invariants such
as reflectance ratios. These lead to more general transfer algorithms for
inverse rendering, and a novel framework for checking the consistency of
images, to detect tampering.
Paper: PDF (PAMI 08)
PDF (ECCV 06)
|

|
Dirty Glass: Rendering Contamination on Transparent Surfaces
EuroGraphics Symposium on Rendering, 2007.
Real-world transparent objects are seldom clean: Their surfaces have a
variety of contaminants such as dust, dirt, and lipids. These
contaminations produce a number of complex volumetric scattering
effects that must be taken into account when creating realistic
renderings. We construct an analytical model for optically thin
contaminants, measure the spatially varying thicknesses for a number
of glass panes of dust, dirt and lipids, and demonstrate renderings
with a variety of volumetric scattering effects.
Paper: PDF
Video
|

|
A Real-Time Beam Tracer with Application to Exact Soft Shadows
EuroGraphics Symposium on Rendering, 2007.
Beam tracing is one solution to efficiently calculate accurate soft shadows
from area light sources. In this paper, we adapt many of the methods for
accelerated ray tracing to develop a real-time beam tracer, that is as fast
as the best ray tracers for primary rays, and up to 30 times faster for
difficult secondary rays, as needed in soft shadows. Moreover, we obtain
reference quality exact shadows, without stochastic noise.
Paper: PDF
Video
|

|
Time-Varying BRDFs
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
13, 3 pages 595-609, 2007.
The properties of virtually all real-world materials change with time,
causing their BRDFs to be time-varying. In
this work, we address the acquisition, analysis, modeling and
rendering of a wide range of time-varying BRDFs, including the drying of
various types of paints (watercolor, spray, and oil), the drying of
wet rough surfaces (cement, plaster, and fabrics), the accumulation of
dusts (household and joint compound) on surfaces, and the melting of
materials (chocolate). Analytic BRDF functions are fit to these
measurements and the model parameters variations with time are
analyzed. Each category exhibits interesting and sometimes
non-intuitive parameter trends. These parameter trends are then used
to develop analytic time-varying BRDF (TVBRDF) models.
Paper: PDF
Video (49MB)
|

|
Viewpoint-Coded Structured Light
CVPR 2007.
We introduce a theoretical framework and practical algorithms for
replacing time-coded structured light patterns with viewpoint codes, in the
form of additional camera locations. Current structured light methods typically use log(N) light patterns, encoded over time, to unambiguously reconstruct N
unique depths. We demonstrate that each additional camera location may replace one frame in a temporal binary code.
Paper: PDF
|

|
4D Compression and Relighting with High-Resolution Light Transport Matrices
ACM Symposium on Interactive 3D graphics, 2007, pages 81--88.
We use a 4D wavelet transform for relighting with all-frequency
illumination. A key observation is that a standard 4D wavelet
transform can actually inflate portions of the light transport matrix.
Therefore, we present an adaptive 4D wavelet transform that terminates
at a level that avoids inflation and maximizes sparsity in the matrix
data. Finally, we present an algorithm for fast relighting from
adaptively compressed transport matrices.
Paper: PDF
Video
|

|
Inverse Shade Trees for Non-Parametric Material Representation and
Editing
SIGGRAPH 06, pages 735-745.
We develop an inverse shade tree framework of hierarchical
matrix factorizations to provide intuitive, editable representations of
high-dimensional measured reflectance datasets of spatially-varying
appearance. We introduce a new alternating constrained least squares framework
for these decompositions, that preserves the key features of linearity,
positivity, sparsity and domain-specific constraints. The SVBRDF is
decomposed onto 1D curves and 2D maps, that are easily edited.
Paper: PDF
Video (24M)
|

|
Real-Time BRDF Editing in Complex Lighting
SIGGRAPH 06, pages 945-954.
In this project, we
develop the theory and algorithms to for the first time allow users to
edit measured and analytic BRDFs in real time to design materials in
their final placement
in a scene with complex natural illumination and cast shadows. The system
can take as input a variety of analytic and data-driven reflectance models,
including the curve-based BRDFs obtained from the inverse shade tree
factorization.
Paper:
PDF (20M)
Video (59M)
|

|
Time-Varying Surface Appearance:
Acquisition, Modeling and Rendering
SIGGRAPH 06, pages 762-771.
We conduct the first comprehensive study of time-varying surface appearance,
including acquisition of the first database of time-varying processes like
burning, drying and decay. We then develop a nonlinear space-time
appearance factorization (STAF) that allows easy editing or manipulation such
as control, transfer and texture synthesis. We demonstrate a variety of
novel time-varying rendering applications using the STAF model.
Paper:
PDF
Video QT (64M)
Video AVI (46M)
|

|
A Compact Factored Representation of Heterogeneous Subsurface Scattering
SIGGRAPH 06, pages 746-753.
Heterogeneous subsurface scattering in translucent materials is one of the
most beautiful but complex effects. We acquire spatial BSSRDF datasets
using a projector, and develop a novel nonlinear factorization that separates
a homogeneous kernel, and heterogeneous discontinuities. This enables
rendering of complex spatially-varying translucent materials.
Paper: PDF (11M)
|

|
Acquiring Scattering Properties of Participating Media by Dilution
SIGGRAPH 06, pages 1003-1012.
We present a simple device and technique for robustly estimating the properties
of a broad class of participating media that can be either (a) diluted in
water such as juices or beverages, (b) dissolved in water such as powders and
sugar/salt crystals, or (c) suspended in water, such as impurities. By
diluting in water, we can measure robustly in the single scattering regime.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Reflectance Sharing: Image-Based Rendering from a Sparse Set of Images
PAMI Aug 06, pages 1287-1302 ,
EGSR 05, pages 253-264
We develop the theoretical framework and practical results for image-based
rendering of spatially-varying reflectance from a very small number of images.
In doing so, we trade off some spatial variation of the reflectance for an
increased number of angular samples. The upcoming PAMI paper also includes a
novel Fourier analysis of spatial and angular coherence.
Paper: PDF
Video (83M)
EGSR 05 (PDF)
|

|
Exploiting Temporal Coherence for Incremental All-Frequency Relighting
EGSR 06. ,
Current PRT methods exploit spatial coherence of the lighting (such as
with wavelets) and of light transport (such as with CPCA). We
consider a significant, yet unexplored form of coherence, temporal
coherence of the lighting from frame to frame. We achieve speedups of
3x-4x over conventional PRT with minimal implementation effort, and
can trivially be added to almost any existing PRT algorithm.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Efficient Shadows from Sampled Environment Maps
JGT 06 11(1):13-36
There are a number of recent methods to importance sample environment maps.
However, these techniques do not exploit the coherence in visibility between
nearby rays. We investigate a number of alternatives and develop a
simple technique that can speed up the rendering of scenes lit by natural
illumination by an order of magnitude with essentially no loss in accuracy.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Modeling Illumination Variation with Spherical Harmonics
Book chapter in Face Processing: Advanced Modeling Methods (pages
385-424, 2006)
The appearance of objects including human faces can vary dramatically with
the lighting. We present results that use spherical harmonic illumination
basis functions to understand this variation for face modeling and recognition,
as well as a number of other applications in graphics and vision.
Paper: PDF
|

|
A Practical Analytic Single Scattering Model for Real Time
Rendering Siggraph 05, pages 1040-1049.
We present a physically-based model that allows for real-time
rendering of a variety of scattering effects like glows around light sources,
the effects of scattering on surface shading, and the appearance with
complex lighting and BRDFs. The model is based on an analytic integration of
the single scattering equations, and can be implemented with simple fragment
programs on modern graphics hardware.
Paper: PDF
Video (74M)
|

|
Efficiently Combining Positions and Normals for Precise 3D Geometry
Siggraph 05, pages 536-543.
We show how depth and normal information, such as from a depth scanner and
from photometric stereo, can be efficiently combined to remove the
distortions and noise in both, producing very high quality meshes for
computer graphics.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Adaptive Numerical Cumulative Distribution Functions for Efficient
Importance Sampling
EGSR 05, pages 11-20
Importance sampling high-dimensional functions like lighting and BRDFs is
increasingly important, but a direct tabular representation has storage cost
exponential in the number of dimensions. By placing samples non-uniformly,
we show that we can develop compact CDFs that enable new applications like
sampling from oriented environment maps and multiple importance sampling.
Paper: PDF
|

|
A Signal-Processing Framework for Reflection
ACM Transactions on Graphics (volume 23(4),
Oct 2004, pages 1004-1042)
We present a signal-processing framework for analyzing the reflected light
field from a homogeneous convex curved surface under distant illumination.
This generalizes many of our previous results, showing a unified framework
for 2D, 3D lambertian, 3D isotropic and 3D anisotropic cases.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Triple Product Wavelet Integrals for All-Frequency Relighting
Siggraph 04, pages 475-485
We propose a new mathematical and computational analysis of
pre-computed light transport. We use factored forms, separately
pre-computing the effects of visibility and material properties.
Rendering then requires computing triple product integrals
at each vertex, involving the lighting, visibility and BRDF. Our main
contribution is a general analysis of these triple products
likely to have broad applicability
in computer graphics and numerical analysis.
Paper: PDF (5M)
Video (17M)
|


|
Efficient BRDF Importance Sampling Using a Factored Representation
Siggraph 04, pages 494-503
We introduce a Monte Carlo Importance sampling technique for general
analytic and measured BRDFs based on a new BRDF factorization.
PDF (8M)
|

|
A Fourier Theory for Cast Shadows ECCV 04, pages I 146-162 ; PAMI Feb 05, pages 288-295
We show that cast shadows can be mathematically analyzed for many simple
configurations, resulting in a standard convolution formula that can be
derived analytically in 2D and analyzed numerically in 3D. The results
help explain many effects of lighting variability in 3D textures and suggest
new bases for that purpose.
Paper: ECCV 04 , PAMI 05
|

|
Practical Rendering of Multiple Scattering Effects
in Participating Media
EGSR 04
Volumetric light transport effects are significant for many materials
like skin, smoke, clouds, snow or water. In particular, one must
consider the multiple scattering of light within the volume.
We develop a general
framework for incorporating analytic point spread functions based on
beam spreading, while considering multiple scattering in inhomogeneous
media.
PDF (2M)
|

|
Using Specularities for Recognition ICCV 03, pages 1512-1519
We present the first method for using specularities as a positive feature for
lighting-insensitive recognition. The method is applied to very difficult
objects like shiny crockery and wine glasses.
Paper: PDF
|

|
Spacetime Stereo: A Unifying Framework for Depth from
Triangulation CVPR 03, II-359--II-366 ; PAMI Feb 05, pages 296-302
We propose a common framework, spacetime stereo, which unifies many previous
depth from triangulation methods like stereo, laser scanning, and coded
structured light. As a practical example, we discuss a new temporal
stereo technique for improved shape estimation in static scenes under variable
illumination.
Paper: CVPR 03 ,
PAMI 05
|

|
All-Frequency Shadows Using Non-Linear Wavelet Lighting Approximation
Siggraph 03, pages 376-381
We present a method, based on pre-computed light transport, for real-time
rendering of objects under all-frequency, time-varying illumination represented
as a high-resolution environment map. For accurate rendering, using non-linear
wavelets is an order of magnitude faster than using linear spherical harmonics,
the current best technique.
PDF (1M) Video (42MB)
|


|
Structured Importance Sampling of Environment Maps
Siggraph 03, pages 605-612
We introduce structured importance sampling, a new technique for efficiently
rendering scenes illuminated by distant natural illumination given in an
environment map.
PDF Video
|


|
Analytic PCA Construction for Theoretical Analysis of Lighting Variability, Including Attached Shadows, in a Single Image of a Convex Lambertian Object PAMI Oct 2002,
pp 1322-1333.
We explain for the first time some classic
empirical results on lighting variability, and take
a first step toward analyzing many classic vision problems
under complex lighting.
Full Paper:
PDF (.8M)
|

|
Frequency Space Environment Map Rendering:
Siggraph 02, pages 517-526
We present a new method for real-time
rendering of objects with complex isotropic BRDFs under distant
natural illumination, as specified by an environment map. Our
approach is based on spherical frequency space analysis.
Full Paper: gzipped PS (4.2M) PDF (3.3M)
|

|
Analysis of Planar Light Fields From Homogeneous Convex Curved Surfaces Under Distant Illumination
Proceedings of Human Vision and Electronic Imaging VI (part of Photonics West, 2001), pages 185--198
This relatively simple to read paper is the first on the reflection is
convolution idea underlying my PhD thesis, and considers the 2D case using
only Fourier transforms.
Full Paper: gzipped PS (.6M) PDF (.2M) Talk: PDF (.8M)
|


|
On the relationship between Radiance and Irradiance: Determining the illumination from images of a convex Lambertian object
Journal of the Optical Society of America (JOSA A) Oct 2001, pages 2448-2459
This paper considers the 3D Lambertian case using spherical harmonics
and derives an analytic formula for the irradiance in terms of the
radiance, including the 9 parameter Lambertian BRDF approximation.
One practical application is interactive rendering with An Efficient
Representation for Irradiance Environment Maps.
Full Paper: PDF (.4M)
Correction: In equation 19, there is a small misprint.
The last term should be ((n/2)!)^2, not
(n!/2)^2
|

|
A Signal-Processing Framework for Inverse Rendering: Siggraph 01, pages 117-128
This paper is the most mathematical so far and derives the theory for
the general 3D case with arbitrary isotropic BRDFs.
It also applies the
results to the practical problem of inverse rendering under
complex illumination.
Full Paper: gzipped PS (3.7M) PDF (1M) Talk: PPT (1.3M)
SIGGRAPH 2002 Course Notes: Acquiring Material Models Using Inverse
Rendering
|

|
An Efficient Representation for Irradiance Environment Maps:
Siggraph 01, pages 497-500
We consider the rendering of diffuse objects under distant
illumination, as specified by an environment map. Using an analytic
expression for the irradiance in terms of spherical harmonic
coefficients of the lighting, we show that one needs to compute and
use only 9 coefficients, corresponding to the lowest-frequency modes
of the illumination, in order to achieve average errors of only
1%.
Full Paper: gzipped PS (3.4M) PDF (1M) Talk: PPT (1.8M) Video
|

|
Efficient Image-Based Methods for
Rendering Soft Shadows:
Siggraph 00, pages 375-384
We present two efficient image-based approaches for computation
and display of high-quality soft shadows from area light sources. Our
methods are related to shadow maps and provide the associated
benefits.
Full Paper: gzipped PS (4M) PDF (1.7M) Talk: PPT (1.8M)
|
 |
Creating Generative Models from Range
Images Siggraph 99, pages 195-204
We have explored the creation of high-level parametric
models from low-level range data.
Our model-based approach is relatively
insensitive to noise and missing data and is fairly robust.
Full Paper: PS (2.5M) PDF (1.5M)
|
 |
Fast
Construction of Accurate Quaternion Splines:
Siggraph 97, pages 287-292.
Dynamic Splines with Constraints for Animation:
Caltech CS-TR-97-03.
We have explored the use of improved numerical approaches
for optimization to automatically create animation from
keyframes. The numerical tools developed
include adaptive refinement based on the Euler-Lagrange
error functional. We have applied this approach to
quaternion splines, greatly speeding up a numerical
method to construct the optimal rotational curve.
Full Paper: Sig 97 PDF
Tech Report
|



























































































































































































































